ESSAY on Critically discuss the differences and similarities between both Durkheim's and Marx's perspectives of punishment.
From the perspective of criminology, punishment can be termed as the sense of a sanction imposed by the legislation of the culprit for criminal offences conducted by them. Punishment must involve the unpleasantness to the victim for an offence which is actually or supposed to be conducted (Ashworth and Roberts, 2013). The provision of punishment has been introduced by criminal law to set an idle example to discourage individuals from getting engaged in such kinds of acts. Sociology of the punishment provides a better framework for the analysis of penal institutions in order to provide a more realistic account instead of considering punishment as an approach used for the control of crime. For this aspect, punishment is considered a complicated social institution from a sociological perspective. This institution is formed by an ensemble of historical and social forces which have a drastic impact on the population of offenders.
Need to Consult Directly With Our Experts?
Contact UsThe concept of punishment is supported by different theoretical approaches given by different criminologists. In this aspect, the main theories are given by Durkheim's and Marx's perspectives of punishment (Brooks, 2012). Émile Durkheim and Karl Marx had different perceptions regarding punishment due to differences in their viewpoint regarding society. According to the perspective of Durkheim, punishment is morally affirming. Along with this, it is grounded by the mechanism of solidarity production. On the other hand, the study of Karl Marx depicts that punishment is an economically conditioned state apparatus (Wright, Tompkins and Mohammad, 2012). As per the approach of Marx, it plays a political and ideological role in the ruling of the dominating class.
However, they both were concerned about the emergence of modern capitalism in society while describing their perspective towards punishment (Easton and Piper, 2012). In accordance with their point of view, criminal activities are highly influenced by evolution in market society and the modern system of division of labour. Both Émile Durkheim and Karl Marx developed their perspectives by considering the impact imposed by the spread of market relations on the reproduction ability of society (Ashworth and Roberts, 2013). Due to this aspect, they both were engaged in the causes and implications of key developments in British society regarding the Industrial Revolution such as the French Revolution.
Approaches given by Durkheim and Marx have important similarities in that these sociologists do not consider punishment and criminal offence as aberrant. As per his point of view, punishment serves a positive function for society (Jewkes and Johnston, (eds.) 2006). Along with this, it reinforces social solidarity and strengthens common values. In addition to this, society reacts actively to severe criminal actions such as paedophilia and murder. For this aspect, Durkheim had outlined a change to restitute justice from retributive justice.
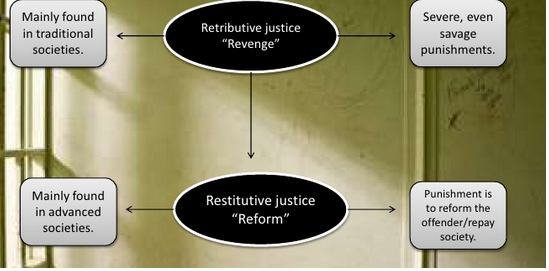
In accordance with the viewpoints of traditional functionalists, people are quite similar to each other due to which society responds to crime more severely. Thus, Durkheim recommended that the penal code should help criminals reform their attitudes or make them repay society (Simon and Sparks, 2013). According to them, punishment is a power that can be used by authorities for the construction of a larger social order. As a consequence, they do not make a direct link between criminal offense the punishment. They consider the theory of punishment within the context of a greater economic and social environment (Ashworth and Roberts, 2013). The second major similarity in both perspectives is that both these theorists were sceptical of the aspects which are outright dismissive on the grounds of justification. Durkheim and Marx had shown their keen interest in the philosophical ramifications in order to make viable changes in the traditional provisions of penal practices.
However, despite of having common objectives, there were certain differences between their theories because of variances in their opinions about the society and environment. Durkheim rejected the contention of punishment in The Division of Labor in Society (1893) (Easton and Piper, 2012). As per his point of view, punishment should have a wider scope regarding vengeance and in providing emotional satisfaction. Further, they described that the social function of punishment is required to provide effect to the emotional outrage of a society whose norms are not complied with by the offender by committing the offensive act (Easton and Piper, 2012). According to Durkheim, a criminal offence can be defined as an action which affects the social consciousness in an adverse manner. As a consequence, criminal functions are used to define the ethical and moral boundaries of social groups (Freiberg and Gelb, 2014). By considering this aspect, punishment is used to provide the reciprocal impact of society's moral generating, maintaining and outraging solidarity that society cannot readily do without.
In the theory given by Durkheim, there is one contemporary manifestation regarding calls for restorative justice. Due to this manifestation, this theory is focused on the injuries and requirements of the community and the victim as a whole instead of considering criminal action or criminal at the core of the punishment. In addition to this, an offender is said to be obliged to these victims and part of the penalty provided by them must include aspects such as an apology to the victim, contribution to the community and direct restitution (O'Mahony, 2012). The objective of this provision was to provide appropriate initiative to the procedure of restoring the solidarity and trust which is breached by the criminal action. Along with this, the approach of restorative justice acts on both aspects i.e. therapeutic consequentialism and retributivism. Further, it also provides a clear alternative to these theories by focusing on the harmed relationships by virtue of criminal action (Easton and Piper, 2012).
Analysis done by Marxists on crime is mainly focused on the political economy of penology. The theory of punishment given by Marxists sought to clarify the practices of punishment by considering the justification provided by their juridical. He had continuously researched legal matters. In addition to this, he criticized the failure of penal theory for consideration of social factors such as poverty and economic inequalities (Wright, Tompkins and Mohammad, 2012). By considering the research framework given by Marx, Georg Rusche and Otto Kirchheimer, they have examined the development of various forms of crime in their paper on Punishment and Social Structure. By considering the social context of crime, Marx also challenged the unequal distribution of punishment on the basis of racial factors by pointing out the disproportion in the number of racial minorities in the statistics of individuals imposed imprisonment.
As per the perspective of Marx, punishment is intended to reinforce the capitalist system and the oppression of working people. According to him, offenses committed by wealthy people are generally ignored or they are lightly punished (Punishment - From Justification To Explanation, 2015). However, the working class has to face harassment and injustice practices. As a consequence, prisons work as a dumping ground for working-class people.
Marx has also been considered as a critique of the political economy. He had provided an attempt to undermine the claim that capitalist organizations and the division of labour are merely the outcomes of general human tendencies to activities of production and exchange (Wright, Tompkins and Mohammad, 2012). The lifelong objective of Marx was to provide refutation to the approach of division of labor with his narrative scope of capitalism. For this aspect, he promoted the account of change in society in order to dismiss the abstract instead of naive individualism underlying the political economy (Garland, 1991). In addition to this, he also provided an attempt to show that class relations are inherently conflictual and on the basis of this aspect, he proved that the capitalist mode of production makes systematic exploitation of one class by another. Thus, according to him, restorative justice is not viable to provide relief to the victim. Due to this aspect, legislation is required to adopt strict practices for the imposition of appropriate punishment to the offender. In addition to this, it will also create awareness among society by which individuals would not get engaged in such kind of activities.
In accordance with the present report, various similarities and dissimilarities have been identified. This study shows that Émile Durkheim and Karl Marx do not consider that punishment is not directly associated with criminal activity. They both have a wider approach regarding punishment as they are focused on social and environmental factors. However, the punishment perspective of Emile was more lenient in comparison to Karl's. It is because, Emile believes that members of a society are in consensus with one another and they all have a common objective. As a consequence, he supported restorative justice instead of providing punishment by considering criminal acts or criminal. On the other hand, the viewpoint of Karl depicts that society is not a peaceful place because there is a constant increase in the activities of contradictions and conflicts. According to him, upper-class people exploit the lower class in order to attain an undue advantage. Henceforth, criminals should be punished with severe punishment by which ideal example can be set for society in order to prevent such kind of actions in the future. Their point of view has been considered in the legal reforms in order to provide better justice to the criminals and to prevent such kinds of activities from society.
References
- Brooks, T., 2012. Punishment. London, United Kingdom: Routledge.
- Easton, S. M. and Pip, C., 2012. Sentencing and punishment: The quest for justice. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
- Jewkes, Y. and Johnston, H., (eds.) 2006. Prison readings: A critical introduction to prisons and imprisonment. Cullompton, United Kingdom: Willan.
- Rusche, G., Kirchheimer, O. and Melossi, D., 2003. Punishment and social structure. New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publishers.
- Simon, J. and Sparks, R., 2013. The Sage handbook of punishment and society. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
- Ashworth, A. and Roberts, V. J., 2013. Sentencing Guidelines: Exploring the English Model. Oxford University Press.
- Easton, S. and Piper, C., 2012. Sentencing and Punishment: The Quest for Justice. Illustrated. Oxford University Press.
- Freiberg, A. and Gelb, K., 2014. Penal Populism, Sentencing Councils and Sentencing Policy. Routledge.
- O'Mahony, M. B., 2012. Accused of murder: supporting the communication needs of a vulnerable defendant at court and at the police station. Journal of Learning Disabilities and Offending Behaviour. 3(2). pp. 77-84
- Wright, N., Tompkins, E. N. C. and Mohammad, Z., 2012. Cross-examination of clinicians at coroners' inquests following deaths in custody. International Journal of Prisoner Health. 8(3/4). pp. 92-98.
Online
- Garland, D., 1991. Sociological Perspectives and Punishment. [Pdf]. Available through: < http://www.umass.edu/legal/Benavides/Fall2005/397G/Readings%20Legal%20397%20G/8%20David%20Garland.pdf>. [ Accessed on 16th October 2015]
- Punishment - From Justification To Explanation. 2015. [Online]. Available through: < http://science.jrank.org/pages/10922/Punishment-From-Justification-Explanation.html>. [ Accessed on 16th October 2015].


 Company
Company













